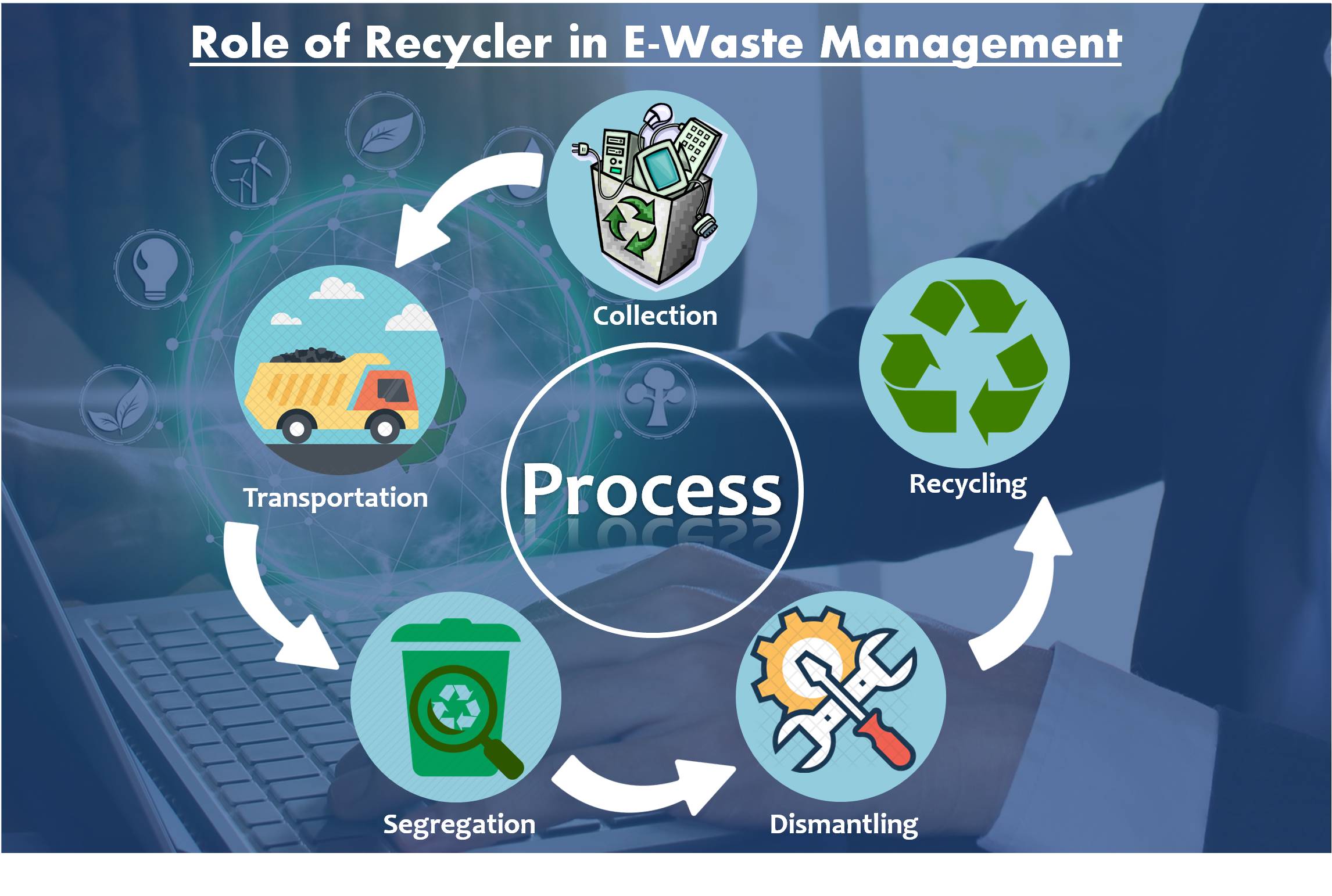
All the Indian manufacturers and importers of Electronic and Electrical Products need to submit a future plan of the proper disposal of the Electronic-Waste in front of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) as the mandatory requirement.
As per the guidelines, manufacturers, and importers needs to tie-up with the authorized recycler to dispose of the E-Waste and submit all the plans related to estimated dump quantity and method adopted for disposal in CPCB to get the EPR Certificate.
E-waste” is a popular, informal name for electronic products nearing the end of their “useful life. “E-wastes are considered dangerous, as certain components of some electronic products contain materials that are hazardous, depending on their condition and density. The hazardous content of these materials poses a threat to human health and the environment. Discarded computers, televisions, VCRs, stereos, copiers, fax machines, electric lamps, cell phones, audio equipment, and batteries if improperly disposed can leach lead and other substances into soil and groundwater. Many of these products can be reused, refurbished, or recycled in an environmentally sound manner so that they are less harmful to the ecosystem. This paper highlights the hazards of e-wastes, the need for its appropriate management, and options that can be implemented.